Semantic Communications for Wireless Sensing: RIS-aided Encoding and Self-supervised Decoding
Published in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023
Recommended citation: Hongyang Du, Jiacheng Wang, Dusit Niyato, Jiawen Kang, Zehui Xiong, and Junshan Zhang. "Semantic Communications for Wireless Sensing: RIS-aided Encoding and Self-supervised Decoding." IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, arXiv:2211.12727 (2022). https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12727
Abstract: Semantic communications can reduce the resource consumption by transmitting task-related semantic information extracted from source messages. However, when the source messages are utilized for various tasks, e.g., wireless sensing data for localization and activities detection, semantic communication technique is difficult to be implemented because of the increased processing complexity. In this paper, we propose the inverse semantic communications as a new paradigm. Instead of extracting semantic information from messages, we aim to encode the taskrelated source messages into a hyper-source message for data transmission or storage. Following this paradigm, we design an inverse semantic-aware wireless sensing framework with three algorithms for data sampling, reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided encoding, and self-supervised decoding, respectively. Specifically, on the one hand, we design a novel RIS hardware for encoding several signal spectrums into one MetaSpectrum. To select the task-related signal spectrums for achieving efficient encoding, a semantic hash sampling method is introduced. On the other hand, we propose a self-supervised learning method for decoding the MetaSpectrums to obtain the original signal spectrums. Using the sensing data collected from real-world, we show that our framework can reduce the data volume by 95% compared to that before encoding, without affecting the accomplishment of sensing tasks. Moreover, compared with the typically used uniform sampling scheme, the proposed semantic hash sampling scheme can achieve 67% lower mean squared error in recovering the sensing parameters. In addition, experiment results demonstrate that the amplitude response matrix of the RIS enables the encryption of the sensing data.
Index Terms: Semantic communications, reconfigurable intelligent surface, wireless sensing, self-supervised learning
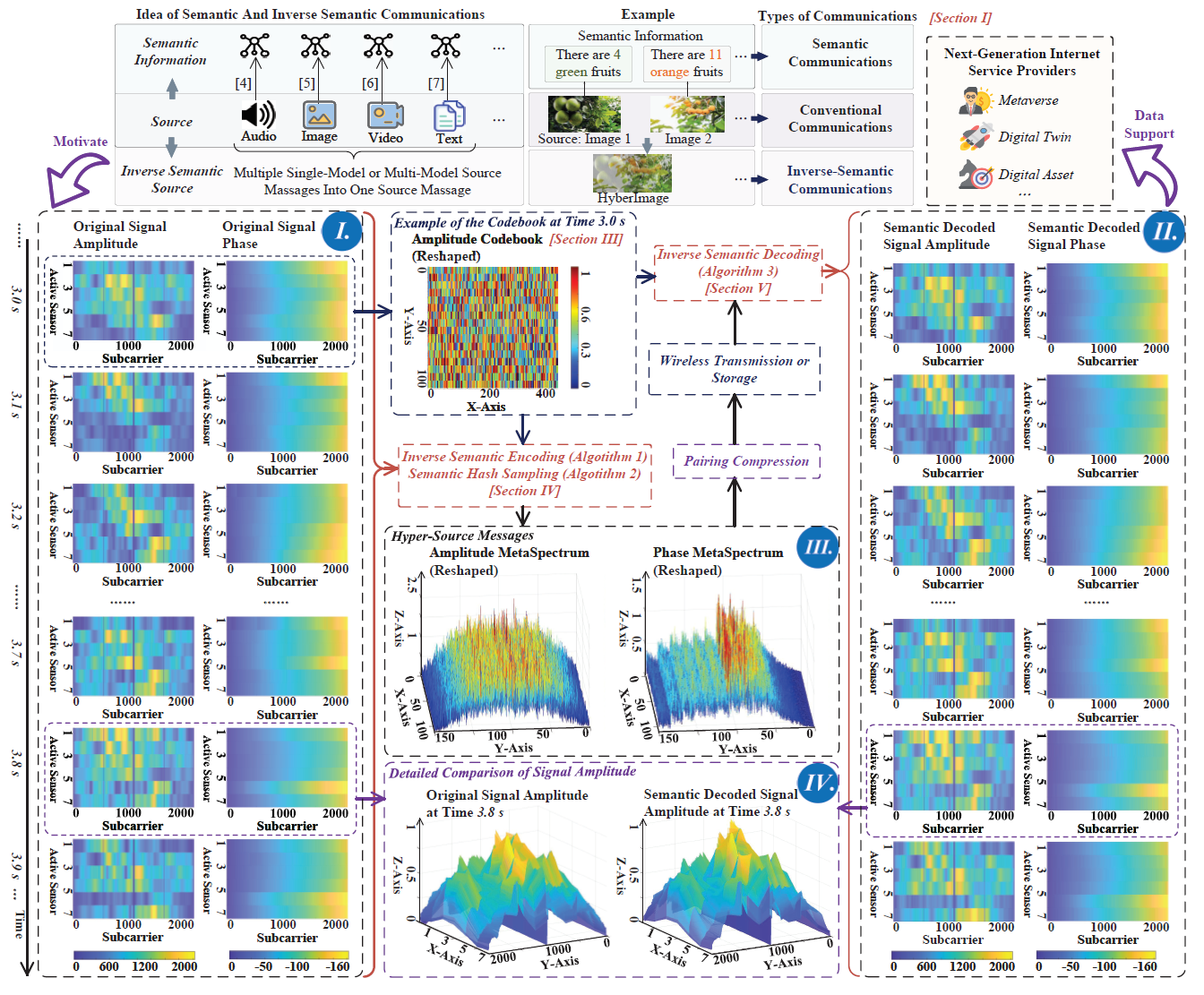
Figure 1: The ideas of conventional, semantic, and inverse semantic communications. Motivated by the inverse semantic-aware communication, we propose an inverse semantic-aware encoding and decoding framework and show the results. Specifically, we select 10 original signal amplitude/phase spectrum (Part I) by using our proposed Algorithm 2, and encode them into one MetaSpectrum by using the RIS and Algorithm 1. After wireless transmission, the reconstruction results (Part II) are obtained by decoding the MetaSpectrum using Algorithm 3. The sensing data is collected by real experiments with an IEEE 802.11ax based test platform [13].
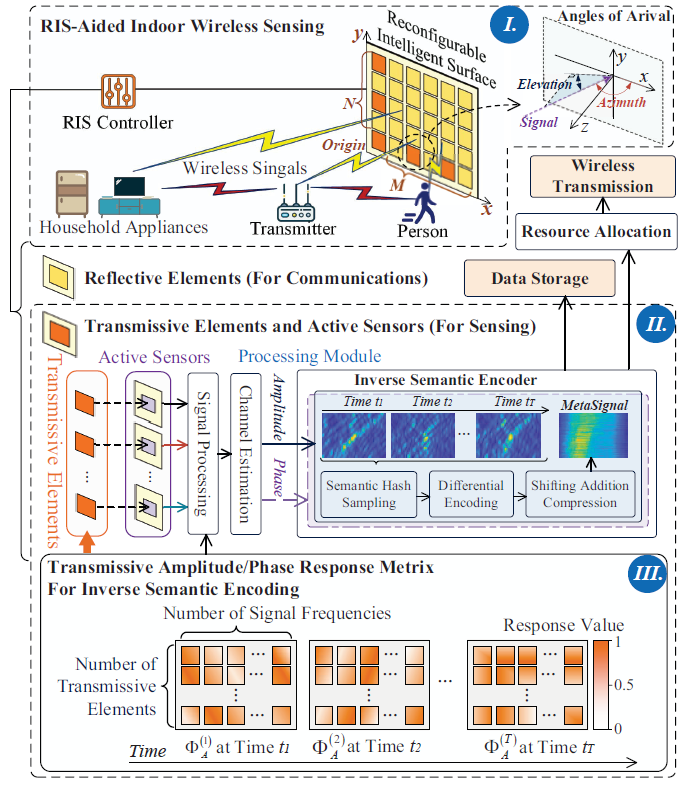
Figure 2: Fig. 2. The framework of the proposed inverse semantic-aware wireless sensing system.
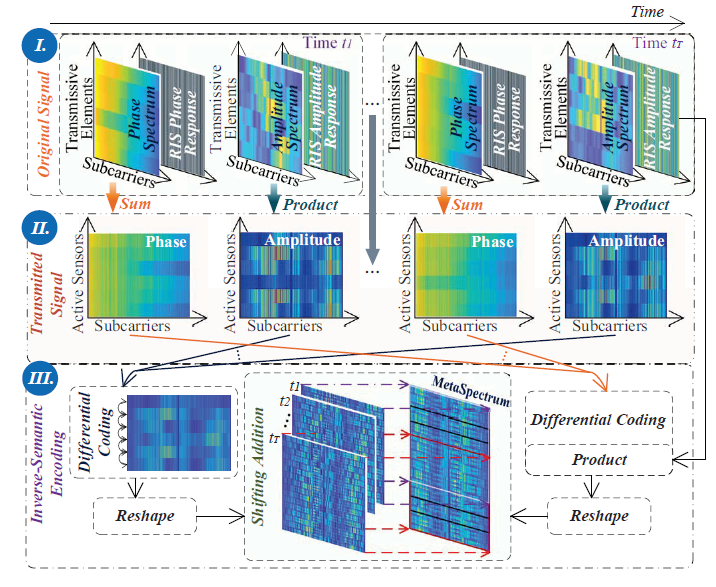
Figure 3: The process of modulating the amplitude and phase spectrums through RIS, and then performing differential encoding and shifting addition.
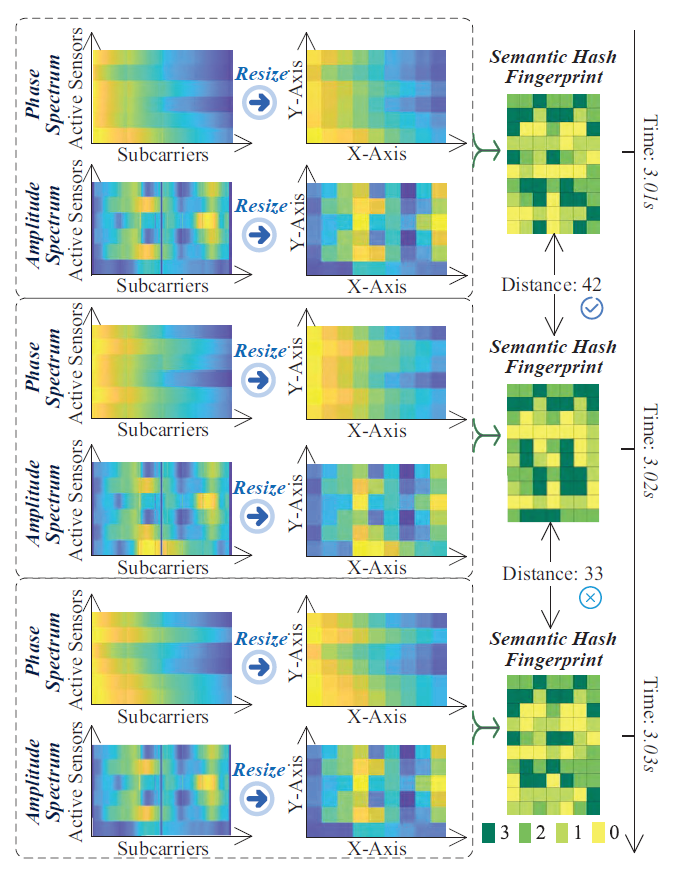
Figure 4: The process of generating the resized matrices from the amplitude and phase spectrums, and then obtaining the semantic hash fingerprint.
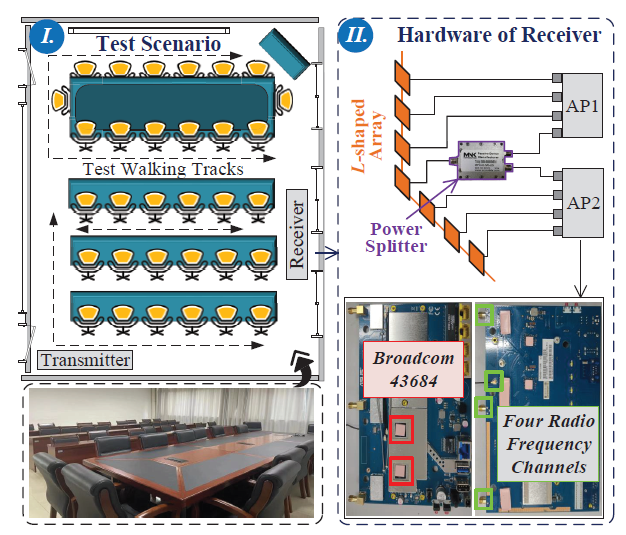
Figure 5: Test scenario and hardware of the receiver.
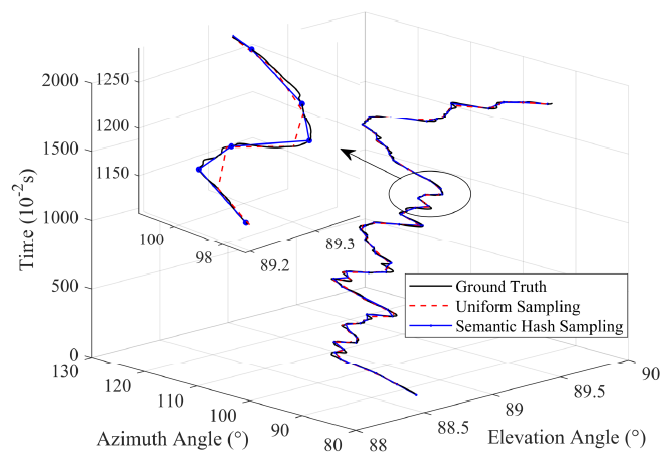
Figure 8: Comparison between different sampling methods and ground truth in terms of 2D AoA changes with movement of human.
